The UK has a diverse housing stock comprising of buildings with lots of different construction types and levels of insulation. The housing stock includes everything from older properties with solid walls (such as Victorian houses) to more modern properties with cavity walls, some of which are the leakiest and worst-performing buildings in the whole of Europe.
In total, there are around 29 million residential properties in Great Britain. Using Government data, roughly 71% of these are classed as having cavity walls whilst the remaining 29% have solid walls constructed of solid brick, stone or other non-standard construction types. Additionally, nearly 87% of properties are thought to have a loft space.
According to the latest household energy efficiency statistics, only 70% of cavity walls are estimated to have cavity wall insulation installed, whilst only 9% of solid walls are estimated to have some form of internal/external solid wall insulation.
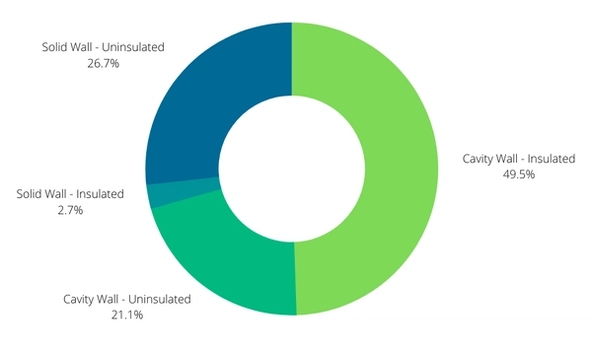
This means that over 47% of the walls in our homes are uninsulated. Meanwhile, only 66% of houses with lofts are considered to have sufficient levels of loft insulation (>= 125mm). When combined with the fact that over a third of the energy used in our homes goes in space heating, insulation plays a significant part in the energy balance of buildings and improving home energy efficiency.
Types of home insulation
Cavity Wall Insulation
Cavity wall insulation is where there is insulation added to the cavity between the internal and external layers of a wall's construction. Modern new-build houses will have wall insulation added during construction as required by building regulations. But many older properties with cavity walls, typically constructed from the 1920s to the 1990s, may have no wall insulation at all.
Cavity wall insulation is installed by drilling holes in the external brickwork and injecting insulating material into the cavity of a wall. Once the insulation has been added, the holes will be filled with cement to match the original mortar. This is a specialist job carried out by cavity wall insulation installers after careful inspection and assessment.
Various insulating materials are used in cavity wall insulation. Fibre insulation is where fibreglass or mineral wool is blown into the cavity using compressed air. Bead-based insulation uses polystyrene beads or granules also blown into the cavity but then bonded together using a resin. Finally, foam insulation uses injected foam mixed using two chemical components which expands to fill the cavity.
Solid Wall Insulation
Where a property has solid walls, there is no cavity inside the wall so it is not possible to use the same cavity wall insulation techniques. Instead, solid wall insulation will mean either adding external insulation to the outside surface of a house or internal insulation to the inside surface of walls.
External Wall Insulation (EWI) comes in various forms but will typically require a layer of insulation board (EPS or XPS polystyrene board) or mineral wool/fibre insulation attached to the external wall surface. The insulation is then be covered using either cladding or render to thermally separate the solid wall from the elements.
Internal Wall Insulation (IWI) uses a number of ways to insulate the internal surface of heat loss walls. Internal wall insulation methods include dry-lining walls or using insulated plasterboard or plaster to retain heat within a building. All forms of internal wall insulation inevitably cause a slight reduction in internal space.
Loft Insulation
Loft insulation is one of the simplest types of insulation to add to houses and is an easy way for homeowners to reduce heat loss through roofs. Roof and loft insulation mean adding insulation material to the roof, attic or loft space of a building trapping heat within and preventing it from escaping through the roof. As we all know warm air rises, so adding loft insulation provides an easy way to reduce energy consumption and lower energy bills.
Insulating lofts and roofs involve adding rolls of glass fibre insulation or polystyrene-based insulation board internally either between the joists of a loft floor or between the rafters of the roof space, or sometimes both. It is a fairly simple process that can be undertaken by the homeowner themselves or by qualified tradespeople.




